Hey there! In this tutorial, we will study what are arrays in c programming and the types of arrays - Single Dimensional Array, Two-Dimensional Array, and Multi-Dimensional Array with the help of a suitable example.
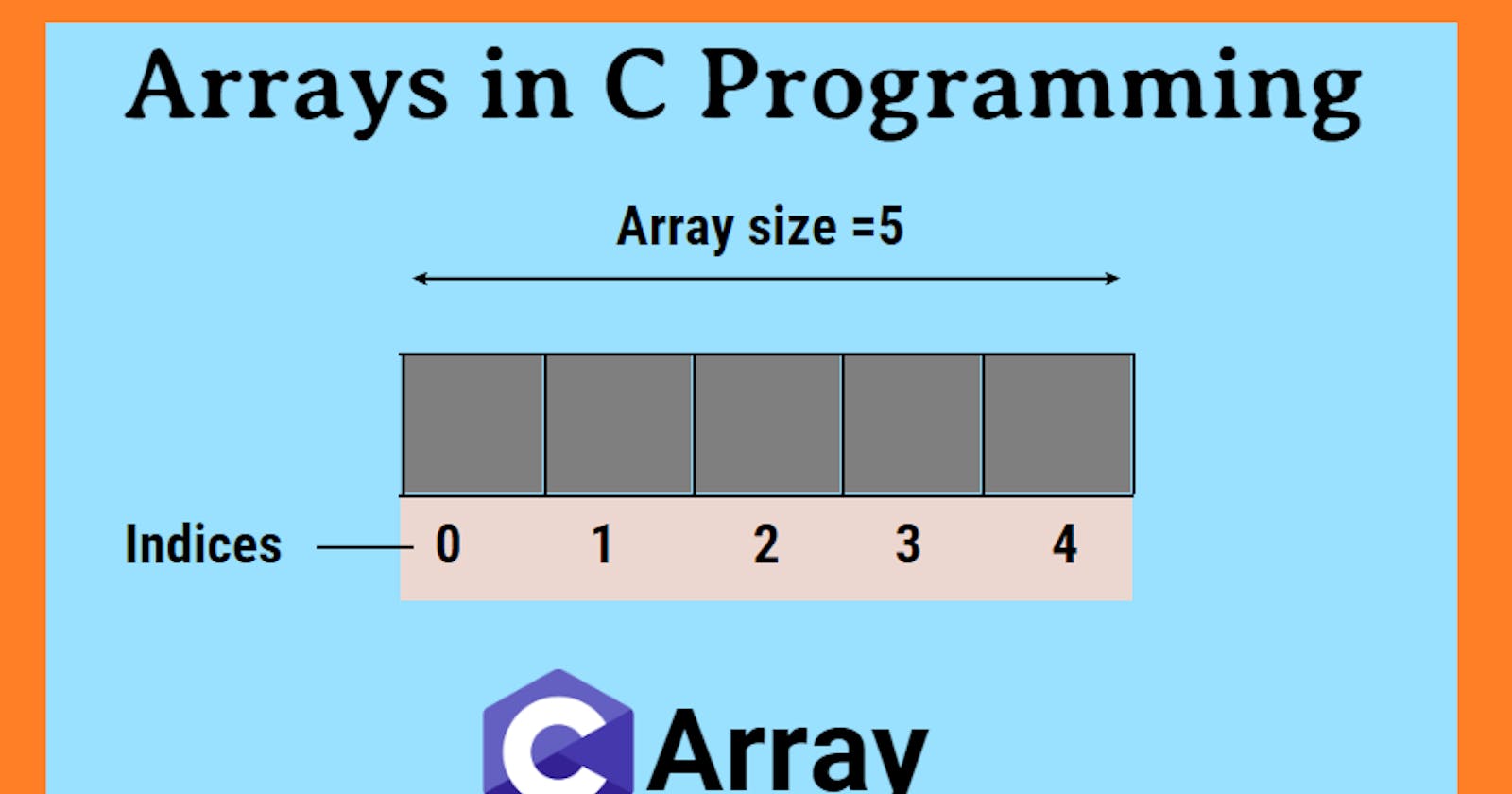
Arrays in C Programming
An array is a primitive and linear data structure that is a group of identical data items, ie it will store only data of only one type or will only store floating-point. Array data is a static data structure, that is, you can allocate memory in compile time itself and cannot change it in run time.
Array live Example
Assume you are creating a program that is to stores the names of the students of a college on the computer and the number of those students is 500. So how will you store the names of these 500 students? You must be thinking in mind that creating 500 variables, doing so will make the program very complex and this method will also take a lot of time and the program will also become very large and there will also be wastage of computer memory space.
To solve this type of problem, c language provides us with Array. With the help of which we solve this type of problem and address it.
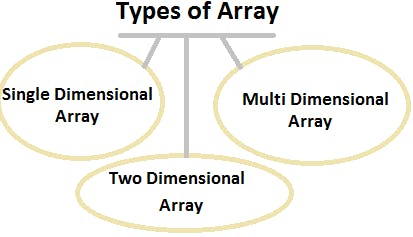
Types of Array
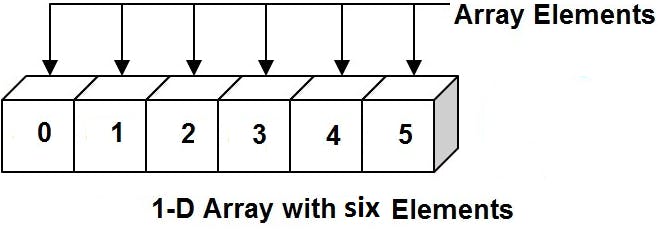
Single Dimensional Array
An array that contains only one subscript is called a one-dimensional array. It is used to store data in linear form. A one-dimensional array is also called a 1-D array.
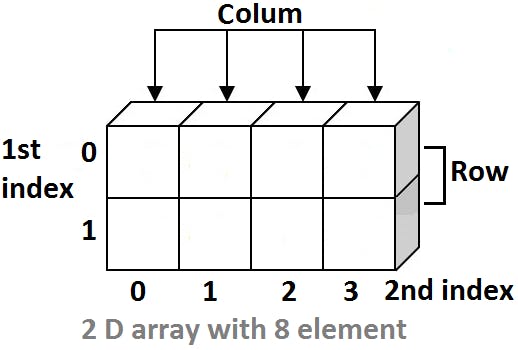
Two-Dimensional Array
An array containing two subscripts is called a two -dimensional array. A two-dimensional array is also called a 2-D array.
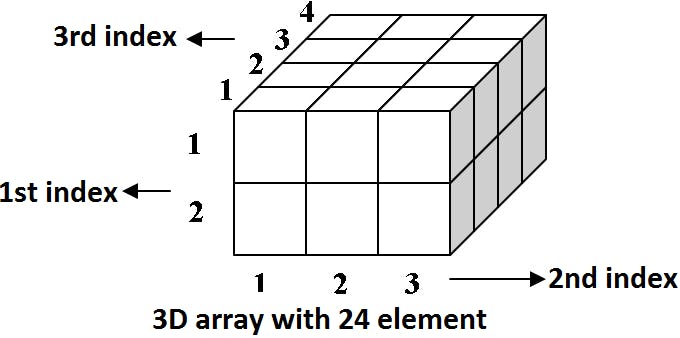
Multi-Dimensional Array
An array containing more than two subscripts is called a Multi-dimensional array. A multi-dimensional array is also called a 3-D array.
Basic program in an array
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[5];
arr[0] = 5;
arr[1] = -10;
arr[2] = 2;
arr[3] = 6;
printf("%d %d %d %d", arr[0], arr[1], arr[2], arr[3]);
return 0;
}
Output
5 -10 2 6